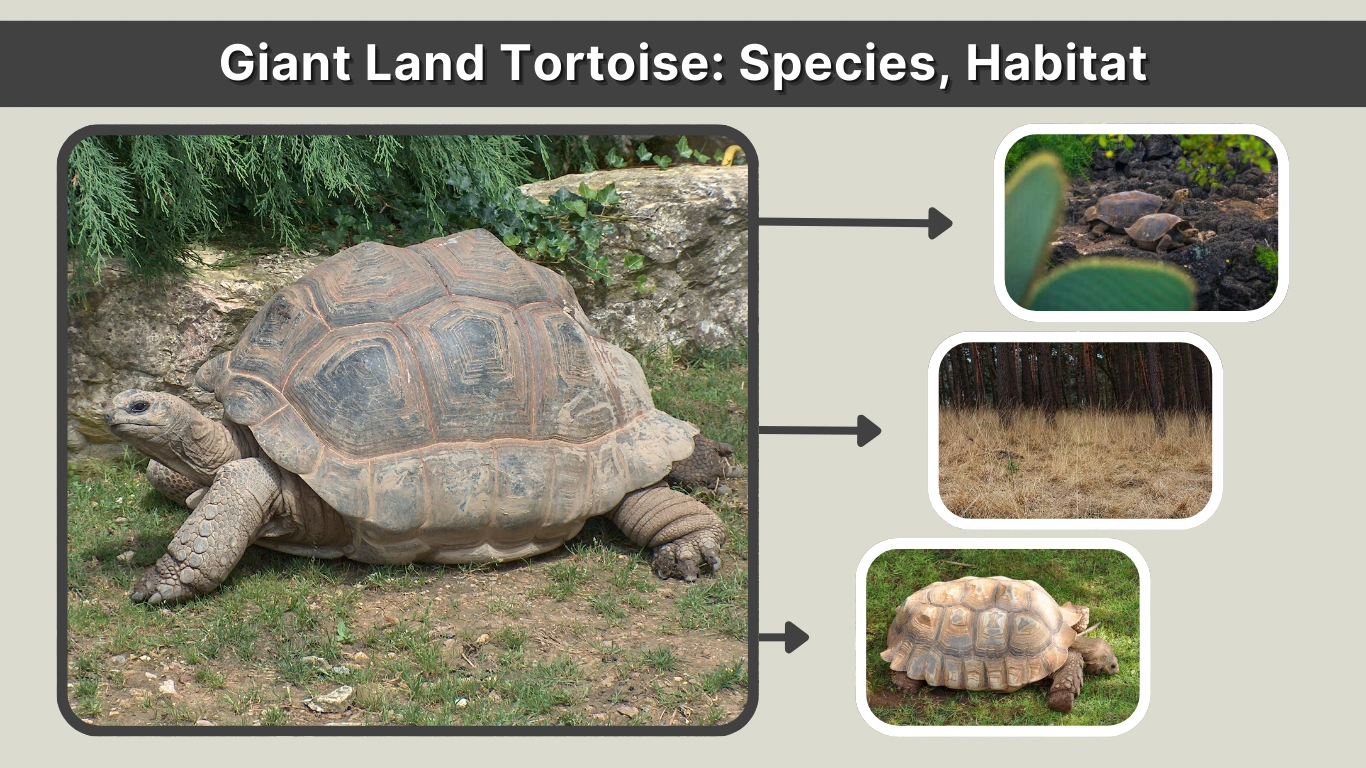
Giant land tortoises are among the largest and longest-living reptiles on Earth. These slow-moving, land-dwelling animals have captured human fascination for centuries due to their massive size, calm behavior, and extraordinary longevity. Found mainly on remote islands, giant land tortoises have evolved unique physical and biological traits that allow them to survive in stable yet challenging environments. Their presence has played an important role in shaping island ecosystems, making them key species in conservation biology. This article explores what defines a giant land tortoise, how to identify one, and the species that still survive today.
What Is a Giant Land Tortoise?
A giant land tortoise is a terrestrial reptile belonging to the family Testudinidae and is distinguished by its exceptional size and long lifespan. Unlike turtles, which are adapted for aquatic life, giant land tortoises live entirely on land and have heavy, dome-shaped or saddle-backed shells. The term “giant” is typically used for tortoise species that can exceed four feet in length and weigh several hundred kilograms.
These tortoises are cold-blooded and rely on external temperatures to regulate their body heat. Their slow metabolism allows them to conserve energy and water, enabling survival in environments where food may be seasonal or scarce. Giant land tortoises are strictly herbivorous and spend much of their day grazing or resting.
Identification of Giant Land Tortoises

Giant land tortoises can be identified by their massive build and distinct features that set them apart from smaller tortoise species. These traits reflect their adaptation to a fully terrestrial lifestyle and long-term survival in stable environments.
Key Identification Features:
- Very large, heavy body with a low center of gravity
- Thick, column-like legs adapted for supporting great weight
- Large shell made of bone and keratin
- Dome-shaped or saddle-backed shell, depending on habitat
- Long neck for reaching ground-level or elevated vegetation
- Wrinkled, leathery skin that reduces moisture loss
- Slow movement linked to a low metabolic rate
These characteristics make giant land tortoises easy to distinguish from other reptiles and highlight their unique evolutionary adaptations.
Giant Land Tortoise Species

Although giant land tortoises were once widespread, only a few species survive today. Most are restricted to isolated islands, where they evolved without large predators.
Galapagos Giant Land Tortoises
The Galapagos Islands are home to several species and subspecies of giant land tortoises. Each island population has adapted to its local environment, resulting in differences in shell shape, size, and neck length. These tortoises are among the most well-known giant land tortoises and can live for over 100 years.
Aldabra Giant Land Tortoise
The Aldabra giant land tortoise is found on Aldabra Atoll in the Indian Ocean. It is one of the largest tortoise species in the world and exists in relatively high numbers compared to other giant tortoises. This species inhabits grasslands, mangroves, and scrub forests and plays a major role in shaping its ecosystem.
Extinct Giant Land Tortoise Species
In the past, giant land tortoises lived on many islands and continental regions, including the Caribbean and parts of the Indian Ocean. Many of these species became extinct due to overhunting and habitat destruction caused by humans. Their loss highlights the vulnerability of giant land tortoises to environmental changes.
Natural Habitat and Distribution
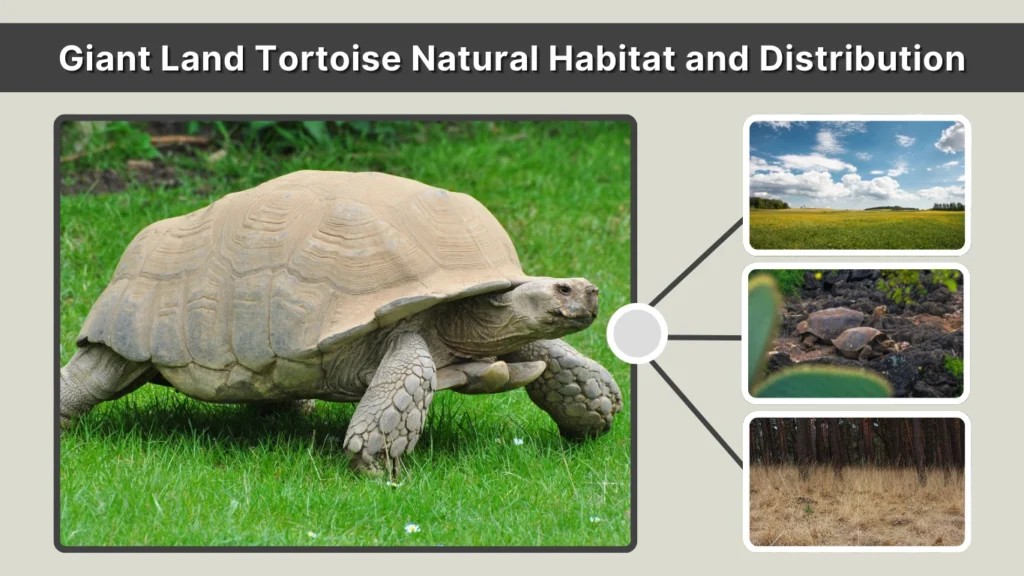
Giant land tortoises are typically found in warm climates with open landscapes and abundant plant life. Most surviving species inhabit islands, where limited predators and stable conditions allowed them to grow large and live long lives. These habitats include grasslands, volcanic plains, and dry forests.
Giant Land Tortoise Diet
Giant land tortoises are strictly herbivorous and rely on a wide range of plant materials for nutrition. Their diet mainly consists of grasses, leaves, shrubs, fruits, cactus pads, and fallen vegetation. Because their habitats can experience seasonal changes, giant land tortoises are highly adaptable feeders, consuming whatever plant matter is available at a given time.
Their strong jaws and sharp, beak-like mouths allow them to tear through tough plant fibers. In wetter seasons, food is abundant, and tortoises feed actively to build energy reserves. During drier periods, when vegetation is scarce, they reduce activity and rely on stored fat and water to survive.
Giant Land Tortoise Lifespan

One of the most remarkable features of giant land tortoises is their extraordinary lifespan. These animals are among the longest-living vertebrates on Earth, with many individuals living for more than 100 years. Some documented cases suggest lifespans of 150 years or longer.
Several factors contribute to this longevity. Giant land tortoises have a slow metabolism, which reduces wear on their bodies over time. Their herbivorous diet, low-stress lifestyle, and lack of natural predators further support long life. In both wild and captive environments, giant land tortoises often outlive multiple human generations.
Why Giant Land Tortoises Live So Long
The slow pace of life plays a major role in their longevity. Low metabolic rates reduce cellular damage, while steady feeding habits provide consistent nutrition. Additionally, their large size offers protection from predators, allowing them to age naturally with minimal physical trauma.
Behavior and Daily Life
Giant land tortoises are calm and non-aggressive animals that follow simple daily routines. Most of their time is spent grazing, resting, and slowly moving between feeding areas. They are more active during cooler parts of the day and often seek shade or mud wallows during intense heat.
Although generally solitary, giant land tortoises tolerate the presence of others and may gather in areas with plentiful food or water. During mating seasons, males may engage in slow, non-violent competition for access to females. Females travel to suitable nesting sites to lay their eggs, which they bury in the soil before leaving to hatch on their own.
Are Giant Land Tortoises Endangered?

Many giant land tortoise species are currently considered vulnerable or endangered. Historical overhunting by sailors and settlers drastically reduced populations, as tortoises were used as a food source during long sea voyages. Habitat destruction and introduced species have further threatened their survival.
Invasive animals such as rats, pigs, and goats can destroy vegetation and prey on eggs and hatchlings, preventing natural population recovery. Climate change also poses new challenges by altering rainfall patterns and food availability.
Human Impact
Human activities have had long-lasting effects on giant land tortoise populations. In addition to hunting, land development and tourism can disrupt habitats and nesting areas. Without active conservation, many populations would struggle to survive.
Conservation and Protection Efforts
Conservation programs have played a vital role in protecting giant land tortoises from extinction. Breeding and reintroduction programs, particularly in the Galapagos Islands, have successfully increased population numbers. Habitat restoration and invasive species control are also key components of these efforts.
Zoos, wildlife reserves, and conservation organizations contribute through research, public education, and funding. Thanks to these combined actions, some giant land tortoise populations are showing signs of recovery.
Giant Land Tortoise vs Other Tortoises
Compared to smaller tortoise species, giant land tortoises grow much larger, live significantly longer, and require expansive habitats. While smaller tortoises may mature quickly and reproduce more frequently, giant land tortoises follow a slower life strategy focused on longevity.
Unlike turtles, which are adapted for aquatic environments, giant land tortoises are fully terrestrial and cannot swim. Their thick legs, heavy shells, and grazing lifestyle clearly separate them from their aquatic relatives.
Interesting Facts About Giant Land Tortoises
Giant land tortoises can survive for months without food or water. Some individuals are capable of recognizing human caretakers and responding to familiar routines. Because of their long lives, they are often seen as symbols of patience, endurance, and wisdom in cultures around the world.
Conclusion
Giant land tortoises are extraordinary animals that showcase the power of slow evolution and adaptation. Their immense size, gentle nature, and long lifespan make them unique among reptiles. However, their survival depends on continued conservation efforts. By protecting their habitats and managing human impact, we can ensure that these ancient creatures continue to thrive for generations to come.
FAQs
What is a giant land tortoise?
A giant land tortoise is a large, terrestrial reptile from the family Testudinidae, known for its massive size, heavy shell, and exceptionally long lifespan.
Where do giant land tortoises live?
Giant land tortoises mainly live on remote islands such as the Galapagos Islands and Aldabra Atoll, where warm climates and limited predators support their survival.
How long do giant land tortoises live?
Many giant land tortoises live for more than 100 years, and some individuals have been recorded living up to 150 years or longer.
What do giant land tortoises eat?
They are herbivores and feed on grasses, leaves, shrubs, fruits, cactus pads, and other plant materials found in their natural habitats.
Are giant land tortoises endangered?
Some species are endangered or vulnerable due to habitat loss, invasive species, and historical overhunting, though conservation efforts have helped several populations recover.